Find out more
Tips on designing a workplace
Just getting up once an hour and taking a few steps to a nearby cabinet or to the coffee kitchen can get your blood circulation back in swing. But often work seems to force you to stay seated. Below you can find some basic tips on how you can nevertheless ensure more physical activity and generally do something for your health or that of your employees.
Provide opportunities to move
Even simple measures can provide opportunities for more movement.
WITH THE HELP OF INTERIOR DESIGN:
- place printers beyond the immediate area within reach.
- put file folders and other documentation outside the direct work area.
- create places for informal communication near the work areas.
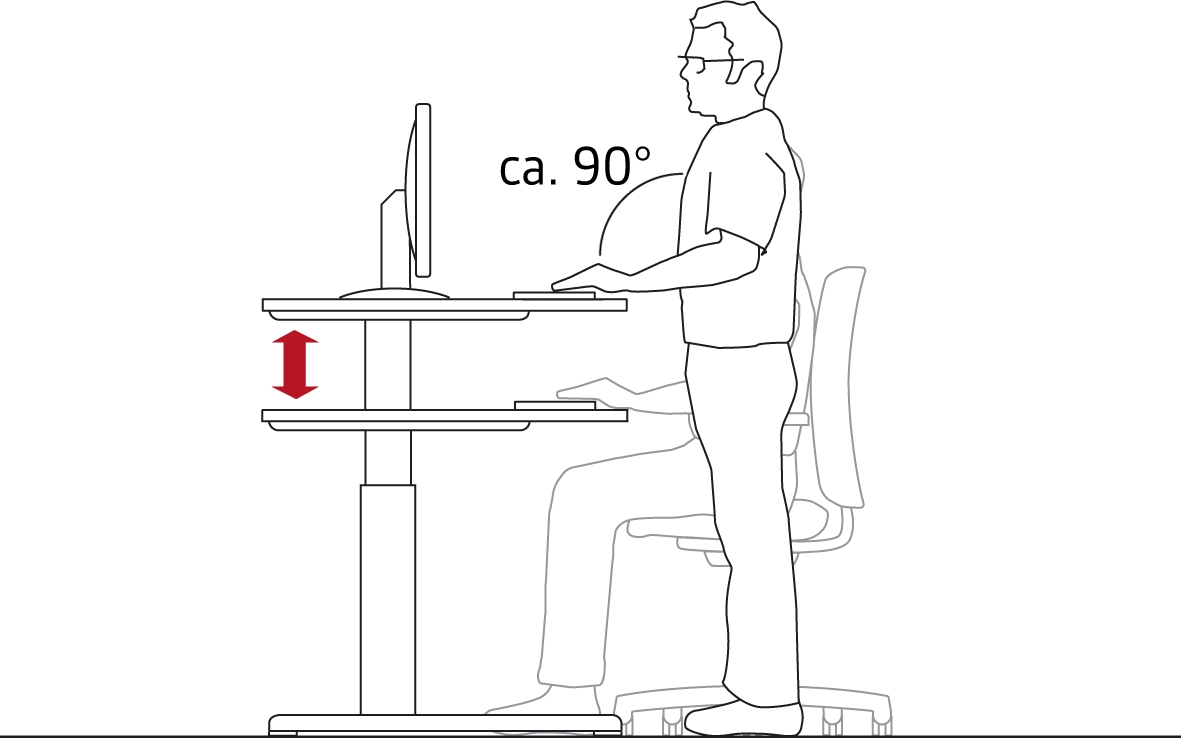
- provide standing desks where employees can do their work.
- provide swivelling office chairs with a synchronization mechanism for dynamic sitting.
WITH THE HELP OF PURPOSEFUL UTILIZATION
- Do as much work as possible while standing, for example phone calls, sorting papers or making notes on your initial creative ideas.
- Frequently manage internal communication through personal talks, go to a colleague’s workplace or exchange a few words in passing or while standing.
- Consciously seek out different places to work for different activities.

Changing the furniture around doesn’t automatically lead to an intensive use of all the possibilities. People have to get used to integrating more movement into their daily work. One way to remind yourself and others to move around more is to use special software that encourages people to stand up, for example. Many companies also train individual employees to become ergonomics experts, who then make sure that meetings are sometimes held standing up and that workplaces are adapted to meet the needs of their users.
Correct posture in the workplace
Starting points for the adjustment of the work place
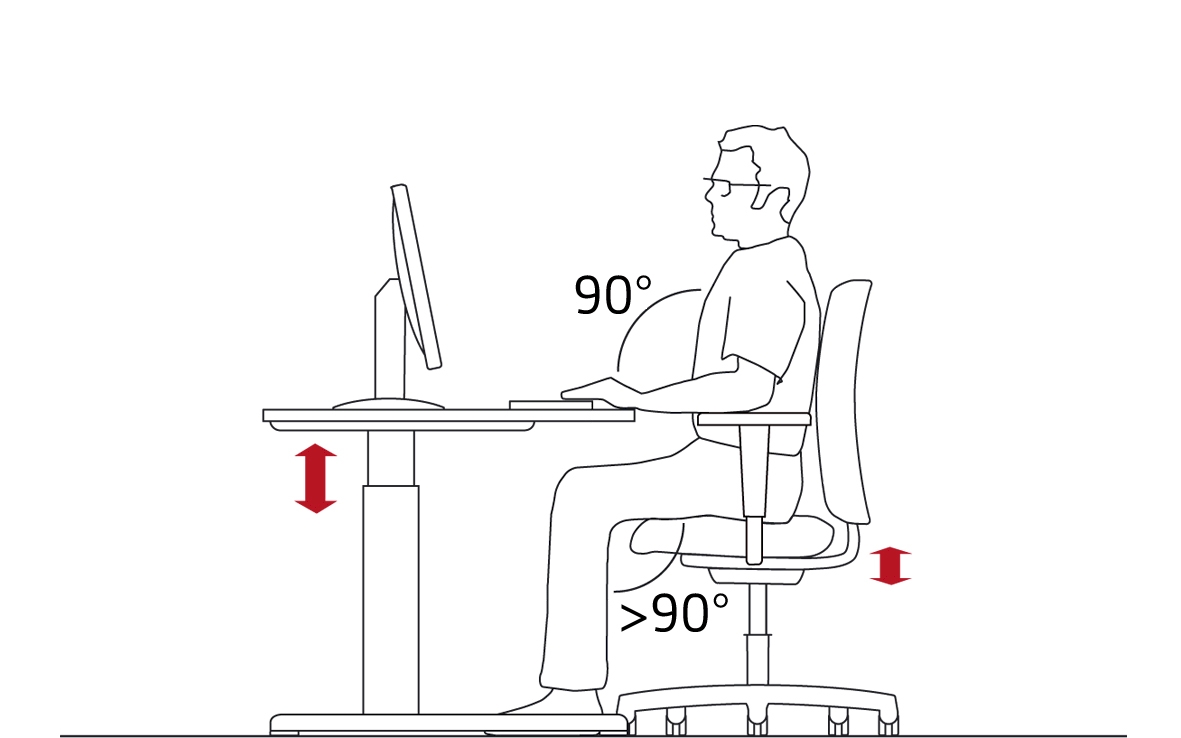
STEP 1: ADJUSTING YOUR OFFICE CHAIR
- Set the seat height so that your thighs and shins form a right angle.
- Adjust the backrest so that your lumbar zone is optimally supported when you are sitting upright.
- If possible, adjust the seat depth and the seat inclination. When adjusting the seat depth, make sure that there is at least half a hand’s breadth of space between the back of your knee and the front edge of the seat.
- Adjust the height of the armrests. With your shoulders relaxed, it should be possible to lightly rest your elbows on the armrests. Your upper arms and forearms should roughly form a right angle.
- If there is a neck support, its height and, if possible, its inclination should be adjusted to optimally support your head when you lean back.
- Adjust the counterpressure of the synchronization mechanism to match your weight.
STEP 2: ADJUSTING THE DESK AND THE MONITOR SCREEN
- Begin by placing the keyboard on the desk. There should be a space of 10 to 15 cm between the keyboard and the front edge of the desk. Some keyboards can be set up at a slight slant. Nonetheless, the inclination should not be greater than 8°.
- Adjust the height of the work table so that when you are using the keyboard your upper arms and forearms continue to form a right angle. Your forearms and the backs of your hands should form a straight line.
- Position the screen so that the distance between your eyes and the screen is at least 50 cm. Depending on the work task and the graphical screen design longer distances may be needed. For safety reasons, when you position the screen make sure that no part of it extends beyond the back edge of the desk.
- Tilt the top of the screen back for a maximum of 35°.
- Adjust the height of the screen so that the top line of characters is maximally at eye level. As a rule, a lower height is more comfortable. That applies especially for wearers of varifocal glasses.
STEP 3: REVIEW THE VIEWING CONDITIONS
Finally, check once again to see that when you are working there is no glare on the screen due to daylight or interior lighting and that the screen is free of light irradiation and reflections.

If the height of your work table cannot be adjusted, begin the adjustment of your workplace with Step 2. The height of your chair will then be adjusted to the height of the work table. The starting point and fixed measurement is the right angle between the upper arm and forearm. If the optimal height of the chair is too high for you to be able to put both feet on the floor comfortably, a footrest will have to be provided.
Avoid stress
Unfortunately, even the best furnishings do nothing to prevent too much workload. But a well-designed working environment can help to make work more efficient and reduce stress.
REDUCE NOISE
Employees are most frequently disturbed by noise, especially by conversations of others.
- Ideally, communicative activities and concentrated work should be spatially separated.
- If you constantly have to switch between different work tasks, you need a well-screened workplace.
- In any case, all office furnishings should include rooms (individual offices or corresponding "cells" in larger rooms) into which you can retreat if necessary.
ENSURE PRIVACY
Retreat should not only be possible acoustically. A visual screening of places for concentrated work should also be provided so that undisturbed work is feasible for everyone. Partition walls or screens that are attached directly to the tabletop are suitable. There is a wide range of shapes and materials. You can find examples in the workstation showrooms at the IBA Forum.
CREATING AN ATMOSPHERE
It is obvious that well-being at the workplace is generally influenced by the design of the furnishings. How the feel-good atmosphere looks, however, varies from company to company and even from person to person. Therefore, we recommend conducting regular employee surveys on their well-being and involving the employees in the design of the workplaces.